Ethanol Diisopropanolamine: A Multifunctional Chemical for Various Industries
Ethanol diisopropanolamine (EDIPA) is an organic compound belonging to the family of alkanolamines, which are known for their dual properties of alcohols and amines. EDIPA is an effective chemical used across several industries due to its multifunctionality and versatility. It is primarily known for its applications in the cement industry, but it also finds use in cosmetics, metalworking fluids, and as a chemical intermediate. This article explores the chemical properties of ethanol diisopropanolamine, its industrial applications, and the benefits it offers to different sectors.
Chemical Structure and Properties of EDIPA
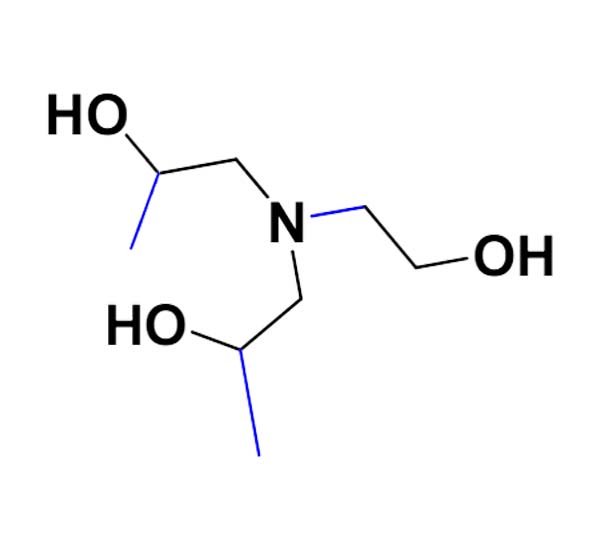
Ethanol diisopropanolamine (C7H17NO3) is a tertiary alkanolamine with a molecular structure composed of both hydroxyl (-OH) and amine (-NH) groups. These groups contribute to its ability to act as a surfactant, corrosion inhibitor, and neutralizing agent. At room temperature, EDIPA appears as a clear or slightly yellow liquid, with a mild amine-like odor.
Key properties of ethanol diisopropanolamine include:
- Molecular Formula: C7H17NO3
- Molecular Weight: 163.22 g/mol
- Density: 1.01 g/cm³
- Boiling Point: 247°C
- Water Solubility: Completely miscible with water and soluble in polar solvents
These characteristics make EDIPA highly adaptable to various chemical processes, which is why it is widely employed in multiple industries.
Use of EDIPA in the Cement Industry
One of the primary applications of ethanol diisopropanolamine is in the cement industry, where it is used as a cement grinding aid and a performance enhancer. Grinding aids like EDIPA play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of the grinding process, reducing energy consumption, and increasing the mill's output. EDIPA's chemical structure allows it to improve the dispersibility of cement particles, reducing the tendency of particles to agglomerate.
1. Cement Grinding Aid
During the production of cement, raw materials such as clinker and limestone are ground into a fine powder. Adding EDIPA to the grinding process helps to prevent cement particles from sticking together. This results in smoother grinding, reduced energy consumption, and increased production output. Additionally, it improves the particle size distribution, which enhances the overall quality of the cement produced.
2. Compressive Strength Enhancer
EDIPA not only acts as a grinding aid but also as a strength enhancer in cement. When added to cement formulations, it accelerates the hydration of clinker minerals, which promotes the early formation of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H), the main binding phase in cement. As a result, the use of EDIPA improves the early and final compressive strength of cement, making it suitable for high-strength applications.
EDIPA in Other Industrial Applications
While EDIPA is predominantly used in the cement industry, it also serves a range of other purposes in different industrial sectors. Some of the most notable applications are outlined below.
1. Surfactant in Cleaning Agents
In the cleaning and detergent industries, ethanol diisopropanolamine is used as a surfactant. Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid, which is essential in cleaning applications. EDIPA helps enhance the effectiveness of cleaning products by allowing water and oils to mix, making it easier to remove dirt, grease, and other impurities from surfaces. This property makes it an ideal additive in household cleaners, dishwashing liquids, and industrial degreasers.
2. Corrosion Inhibitor in Metalworking Fluids
Ethanol diisopropanolamine is commonly used as a corrosion inhibitor in metalworking fluids, cutting oils, and lubricants. It forms a protective barrier on metal surfaces, which helps prevent oxidation and corrosion, extending the lifespan of metal tools and machinery. In this application, EDIPA is particularly valuable in industries where prolonged exposure to moisture and chemicals could lead to rust formation and material degradation.
3. pH Adjuster in Cosmetic Products
In the cosmetic and personal care industry, ethanol diisopropanolamine is used as a pH adjuster and emulsifying agent. Many cosmetic formulations, such as creams, lotions, and shampoos, require a stable pH level to maintain product integrity and ensure skin compatibility. EDIPA helps regulate the pH of these products while also stabilizing emulsions, keeping oil and water components from separating.
4. Intermediate in Chemical Synthesis
As an intermediate in chemical synthesis, EDIPA serves as a building block for producing other chemical compounds. Its dual functionality as both an alcohol and an amine allows it to participate in a variety of reactions, making it a valuable component in the manufacture of surfactants, agrochemicals, and pharmaceutical products.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
While ethanol diisopropanolamine is generally regarded as a safe chemical when handled properly, there are some important safety precautions to consider. Prolonged exposure to EDIPA, particularly in its concentrated form, can cause skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of vapors or mist may lead to respiratory discomfort. It is recommended that workers handling EDIPA wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection when necessary.
In terms of environmental impact, EDIPA is considered biodegradable, meaning it will naturally break down in the environment over time. However, as with any chemical, it is essential to follow local disposal regulations and avoid releasing EDIPA directly into water sources to prevent contamination.
Conclusion
Ethanol diisopropanolamine is a multifunctional chemical compound that plays a vital role in various industries. Its use as a cement grinding aid and strength enhancer makes it indispensable to the construction industry, while its properties as a surfactant, corrosion inhibitor, and pH adjuster allow it to be employed in cleaning products, metalworking fluids, and cosmetics. The versatility and adaptability of EDIPA make it a highly valuable compound for industrial processes. As industries continue to evolve and seek more efficient solutions, ethanol diisopropanolamine is likely to remain a key player in many sectors.